The arsenal of dental materials and tools is updated daily with new products. Each innovation is designed to make dental treatment more effective, as comfortable and durable as possible. Some methods of treatment that have been used for quite a long time and were actively used until recently, on the contrary, are losing their relevance. One of them is dental treatment using a resorcinol-formalin mixture. For about a century, this technology was considered effective, until experts revealed its negative consequences not only for teeth, but also for the body as a whole.
How resorcinol-formalin mixture works
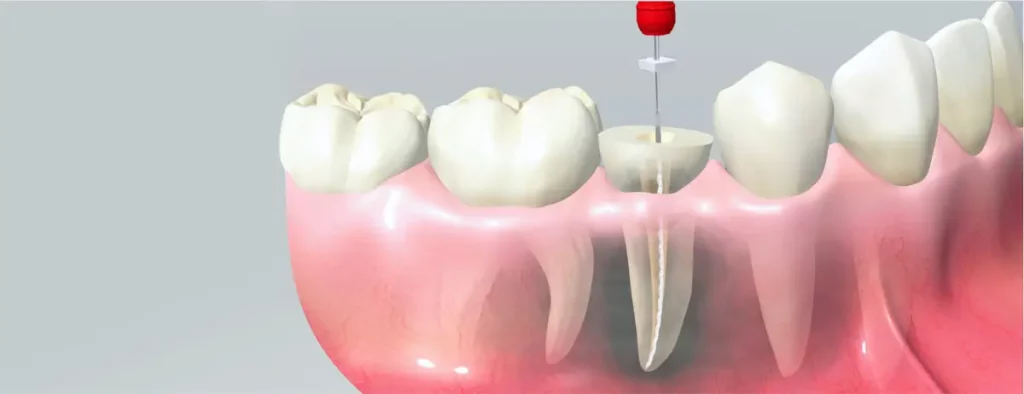
The essence of this technique is that the mixture of formalin and resorcinol has a high diffusion property, so there is no need to pass the root canal with instruments to the top. It is enough to enter the composition on ¾ of the channel. The rest of the pulp in the removed branches will be mummified and disinfected under the influence of a resorcinol-formalin mixture. Under the influence of Albrecht’s mass, the necrotic remains of the pulp are converted into a polymer-like substance, and the hardened mass does not allow moisture, microorganisms and other external agents to pass through.
Until the beginning of the last century, this method of filling root canals was widely popular in the treatment of pulpitis and periodontitis. And there were reasons for this: a simple and inexpensive procedure made it possible to reduce the risk of possible complications after tooth treatment to a minimum.
Cons of using resorcinol-formalin mixture
Despite all the advantages of the method of filling root canals with a mixture of resorcinol and formalin, over time, such consequences were found that became a good reason for many specialists to refuse to use it. Currently, dentists do not use this technology at all.
According to the observations of dental practitioners, several years after root canal filling with RFS, in the vast majority of patients, the teeth became brittle and brittle, changed color (from pink to brown), atrophy of the gums and exposure of the roots of the cured tooth were observed.
It has been proven that the resorcinol-formalin mixture does not provide a hermetic sealing of the root canal, and this can lead to the development and spread of the infectious process. Since the pulp is completely inactivated by the mixture, patients did not experience pain in the tooth even with inflammatory changes in it. As a result, noticeable signs of inflammation became apparent when the process worsened: the complication spread to adjacent teeth or surrounding tissues.
Over time, scientists have found that the harm caused to the body by a mixture of resorcinol and formalin is far from local. Studies have shown that both of these substances have a pronounced toxic effect on the body as a whole and can be carcinogens in relation to the kidneys, liver and other organs.
“Red Russian” was the name of the teeth treated with the help of RFS from our fellow emigrants by foreign dentists. Changing the color of the teeth after filling with a resorcinol-formalin mixture was an extremely unpleasant and unexpected consequence for patients, especially those who treated the anterior group of teeth using this technique. Experts have found that whitening procedures are ineffective in this case, since the color of the dentin changes, and due to the fragility of the enamel, their use is fraught with chips on the teeth.
A large percentage of teeth treated with the resorcinol-formalin method need to be re-treated after some time, but it is rather difficult to predict the result. This is due to the fact that the mixture hardened in the channels is not visible on the x-ray, so it is impossible to assess the quality of the filling, to see the voids. Plus, the channels sealed with a resorcinol-formalin mixture have to be unsealed in several stages using mechanical and chemical effects. The fragility of the walls of such a tooth is an obstacle to installing a large filling. The prognosis will depend not only on the preservation of dentin and roots, but also on the state of periodontal tissues.
All these nuances significantly complicate the preparation of a treatment plan. The prognosis in this case will depend not only on the safety of dentin and roots, but also on the state of periodontal tissues. If quality treatment is difficult, the tooth has to be removed.