Like any science, dentistry does not stand still. Something new is constantly appearing in it, which improves the quality of work of dentists. We made a selection of the most impressive technologies that are used in modern clinics.
- Dental microscope
Allows the doctor not to work “by touch”, but to see what he is treating. As a result, the accuracy of manipulations increases significantly, and the treatment time is reduced.

Microscopes are used in therapeutic, orthopedic and surgical dentistry. But this equipment is most in demand in the treatment of tooth canals. Under 8-20-fold magnification, the dentist achieves perfect canal filling, which reduces the risks of possible complications to zero. For comparison: with microscopic endodontic treatment, problems develop in the future in 30-40% of patients.
- Device for detecting hidden caries Diagnodent
The accuracy of diagnosing caries using a dental probe is about 50%, using an X-ray examination – 60%. And when checking the tooth with the Diagnodent method, it increasesup to almost 90% .
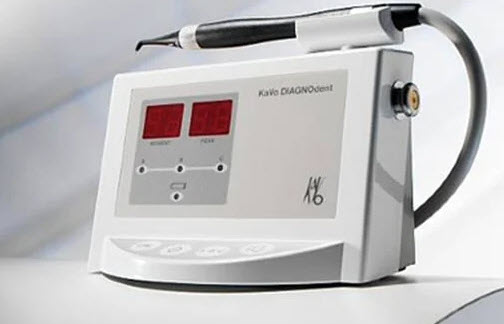
The operation of the device is based on the use of laser light. Getting on the crown of the tooth, it is scattered differently by healthy and softened (i.e., affected by caries) tissues. The sensors of the device capture changes, process them and transform the result into a sound signal and numbers on the screen. With the help of Diagnodent, the doctor can detect caries anywhere in the tooth and at any of its stages – even at the earliest stage, which both the eye and the “X-ray” miss.
- Composite materials
Most patients are aware of composite fillings. But in general, the range of applications of these materials is much wider. They are also used to make dental inlays, veneers, and sometimes even crowns and bridges.
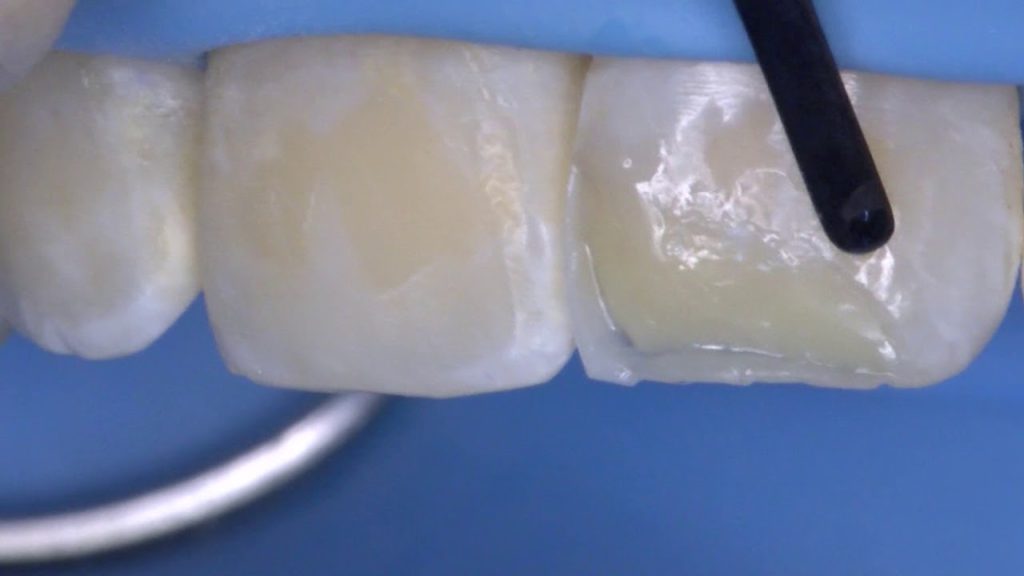
The main advantage of composites is in a wide variety of shades, from which the doctor can easily choose the option that is most suitable for the color of the patient’s natural teeth. In addition, the translucent properties of the materials allow the creation of very natural, invisible restorations.
The service life of composite fillings and veneers is more than 5 years, inlays – more than 10. Crowns and dentures made of composites are usually regarded as temporary, but with good care they can also last a long time.
- Intraoral cameras
If earlier, to examine the inner surfaces of the teeth, dentists used a mirror, but now intraoral cameras perfectly cope with this task.
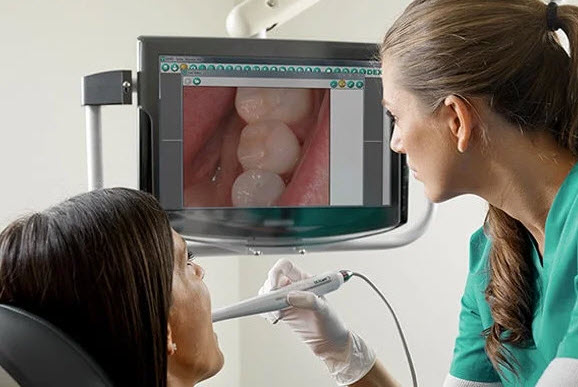
The size of such cameras is slightly larger than a pencil. Information from them is immediately transferred to the computer. On the screen, the doctor sees all the structures in an enlarged view and, if necessary, can show and explain something to the patient. An intraoral camera can take digital pictures and videos.
- 3D printing of dental restorations and prostheses (CAD/CAM technology)
This technology allows the production of ceramic inlays, veneers, crowns or bridges directly in the presence of the patient. The peculiarity of the procedure is that the entire process of creating restorations is controlled by a computer. Using an intraoral scanner, the dentist takes digital “casts” of the teeth, which are then processed by a computer program. According to the obtained three-dimensional model of the teeth on the CEREC device, a dental restoration is machined from solid blocks of zirconium dioxide or ceramics, which ideally matches the shape and location of the patient’s teeth.
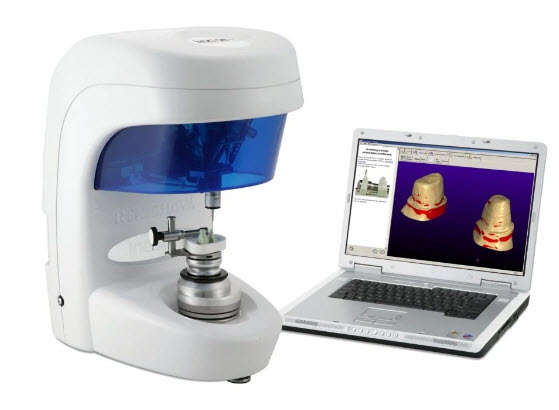
Immediately after turning, prostheses or micro-prostheses are installed to the patient. The participation of a dental technician in this work is not required.
- Air abrasive treatment
An alternative to traditional “drilling” of a tooth in the early stages of caries . The affected area of the tooth is subjected to a gentle treatment with a jet of compressed air with aluminum oxide microparticles. Softened tissues are removed from the surface of the tooth, while healthy ones remain intact. At the same time, the tooth does not overheat, the patient does not feel any unpleasant odors, sounds, and most importantly, pain. Anesthesia in air-abrasive treatment is not required in most cases.
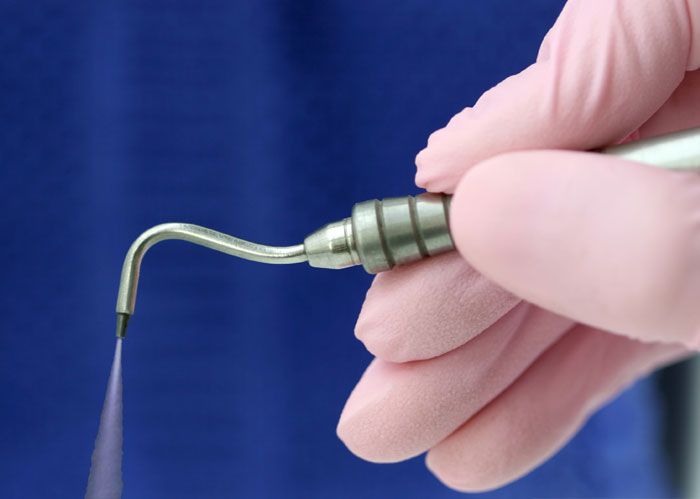
The method is also used to polish and grind old fillings and remove stains from the surface of the teeth.
- Digital X-ray diagnostics
Compared to analog (film) “X-ray”, digital has several advantages. First: reduced radiation exposure (for targeted x-rays – only about 1-3 μSv, for panoramic ones – no more than 20 μSv). Second: high definition and contrast of images (X-ray images are obtained without distortion). And thirdly, digital images can be processed on a computer – for example, to enlarge certain areas in order to take a closer look at them.
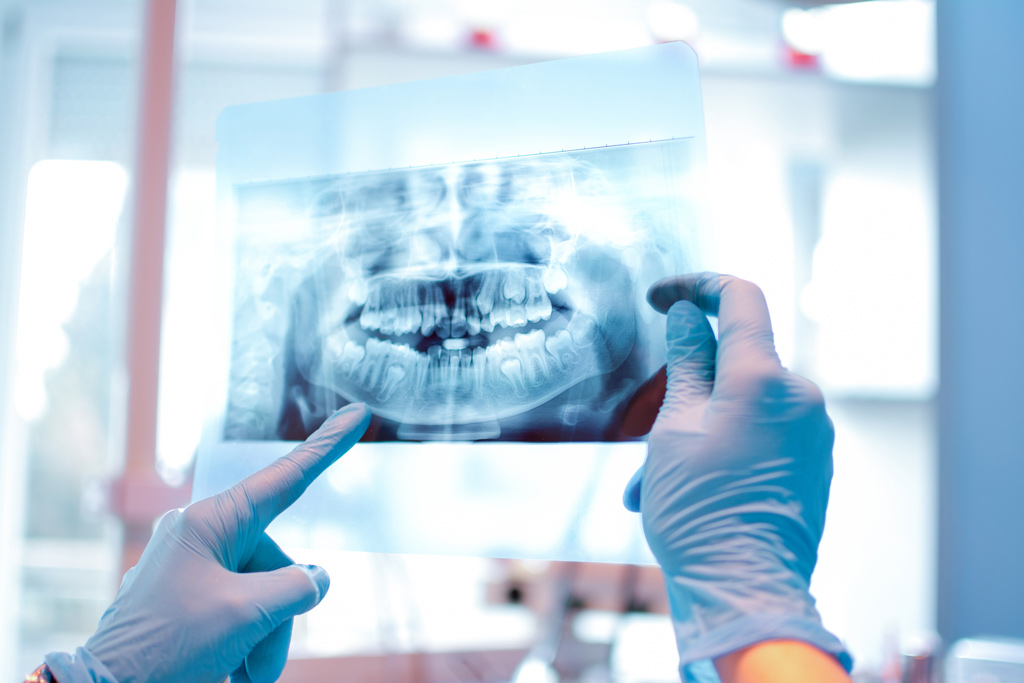
In addition, if earlier, in order to take a picture of one tooth, the patient had to be sent to the X-ray room, now such studies are carried out right in the dentist’s chair. For this, a mobile digital X-ray machine is used – a radiovisiograph, which practically does not irradiate the patient.
- Dental implants
A dental implant is essentially a screw that is placed in the socket of a missing tooth. From above, it is covered with an artificial crown made of metal ceramics, zirconium dioxide or solid ceramics. As a result, the patient receives a tooth that looks and functions like a real one. Implants differ from traditional prostheses in that they do not load healthy teeth and do not require their processing. Chewing load from them is transferred to the jaw bone, as well as from natural teeth.
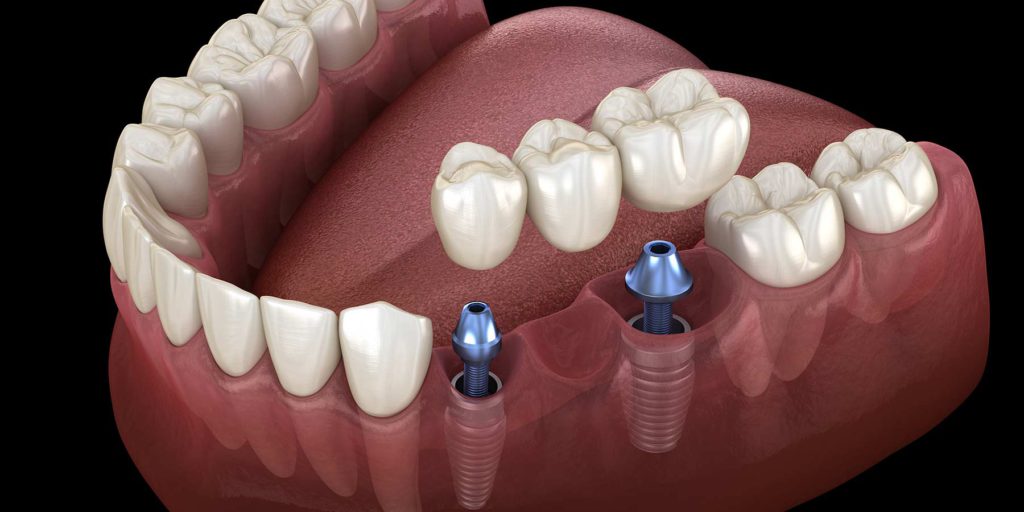
In general, dental implants were invented a very long time ago. But models with high rates of survival began to appear only about 20 years ago. The rejection rate of modern implants does not exceed 3-5%.
- Dental lasers
Laser technologies are used in their work by dentists and surgeons. Lasers are used to diagnose latent caries (Diagnodent method), cure composite fillings, some whitening procedures and treat caries in the early stages (when the disease has not yet gone beyond the enamel). Similar to air-abrasive devices, laser ones gently remove tissues affected by caries without affecting healthy ones.
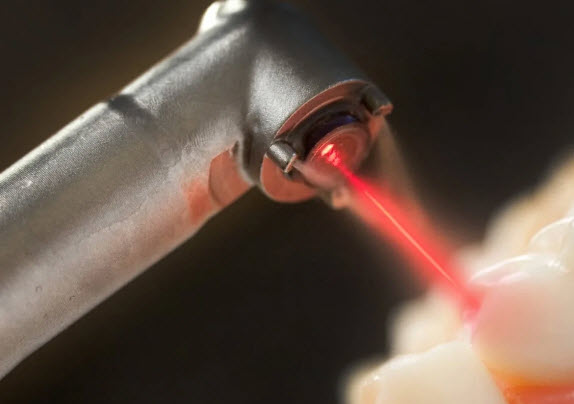

In surgical dentistry, laser instruments are used as an alternative to traditional scalpels.