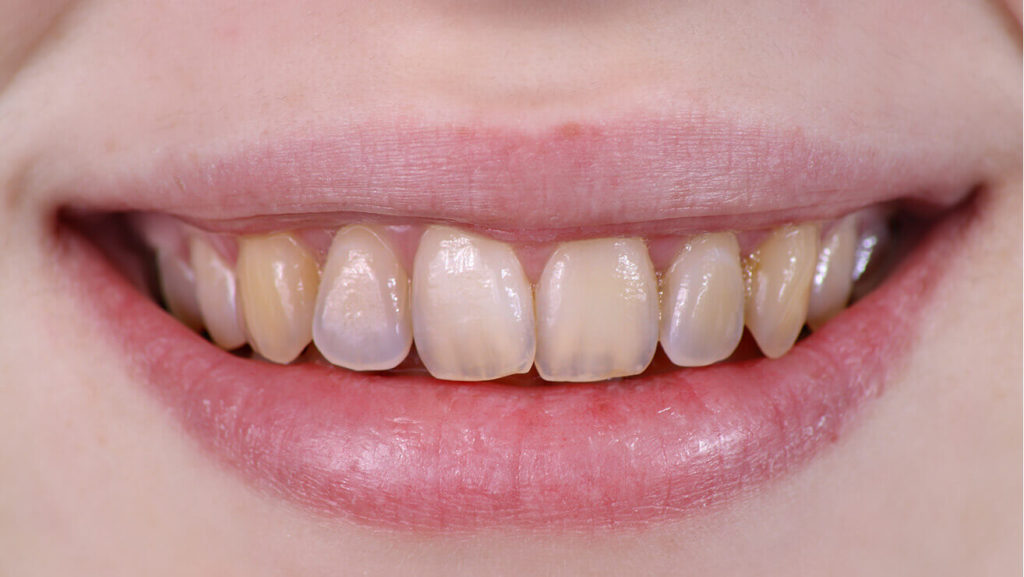
Erosion of tooth enamel is a common non-carious lesion, accompanied by thinning of the enamel and dentin layer. As a rule, this disease is located symmetrically in the oral cavity: on premolars, canines or incisors. As a result of erosion, visible cosmetic defects appear on the teeth. In addition, the problem leads to pain when eating and drinking, brushing your teeth, exposure to cold air, chemical irritants, etc.
If signs of erosion are found, it is recommended to start treatment immediately, since the lack of treatment aggravates the enamel defect and can lead to complete loss of enamel on the outer surface of the tooth. Surfaces on which erosion develops gradually begin to be pigmented.
Causes of the disease
Doctors have not yet established the exact factors for the occurrence of this disease, since it can manifest itself in almost any person, but experts have settled on the following options:
- Mechanical. Explains the manifestation of the disease by excessive mechanical stress exerted on the teeth. For example, brushing your teeth with an excessively hard brush, using too often a whitening abrasive paste or powder at home, you can scratch the tooth, which will lead to erosion;
- Chemical. Researchers who adhere to this theory call the main causes of dental erosion the effect on the enamel of products with an increased level of acidity;
- Endocrine. The concept is based on the results of studies that have found a relationship between erosion and hyperfunction of the thyroid gland. It is known that people suffering from thyrotoxicosis are twice as likely to visit a dentist because of dental erosion;
- Increased load on the dentition, when, with an incorrect bite or the absence of individual units, the chewing function is performed unevenly;
- Some medications can also cause enamel erosion as a side effect;
In industries with metal or mineral dust, as well as when working with chemicals.
More precisely, the causes of the disease can be determined with complex hardware diagnostics.
At-risk groups
The biggest risk groups by age are people from 40 to 60 years old, but children also often suffer from erosion.
How to treat?
As part of the course of treatment, both local and general therapeutic manipulations are used. After the dentist identifies erosion on the enamel, you may need additional consultation with a gastroenterologist and endocrinologist. The main task of the dentist is to stabilize the tooth enamel and stop the thinning of the hard tissues of the teeth. For this purpose, remineralization and saturation of the enamel with calcium and fluorine is carried out. In addition, a course of vitamins is prescribed.
Stages of erosion of tooth enamel
There are three stages of tooth enamel erosion:
- Initial. This stage is very difficult to notice on your own. Usually, at the initial stage, the dentist notices erosion, since only in some parts of the tooth the enamel loses its luster and changes its shade;
- Average. Teeth begin to react to cold, hot, salty and sweet, pigmentation becomes visually noticeable;
- Deep. The enamel is almost completely destroyed, in yellow and brown pigmentation.
There are 2 forms of tooth erosion. The active form is characterized by a rapid course of the disease, a change in the structure and color of the enamel. The stable form is almost asymptomatic, since in this case the body itself produces dentin to protect the affected areas of enamel.
Treatment Methods
- Therapeutic. Vitamin complexes with fluorine and calcium are prescribed;
- Polishing and strengthening with special pastes with therapeutic compounds to strengthen the enamel;
- Remineralization. Teeth are covered every day with pastes, which include calcium, fluorine, phosphorus, zinc and other components that heal the enamel;
- Electrophoresis. A procedure that saturates the teeth with nutrients;
- Sealing. Some enamel defects can be closed with filling materials
In case of serious irreversible damage, the lack of hard tissues is compensated by veneers, artificial crowns and composite materials.
The main thing when this problem is detected, you do not need to self-medicate and fight erosion with traditional medicine. Since in this case it is only possible to aggravate the situation, and it is impossible to stop the thinning of the enamel by such means.
Treatment Prevention
- brushing your teeth twice a day;
- use of toothbrushes with natural bristles, soft or medium hardness;
- the use of high-quality toothpastes with a high fluoride content to strengthen and mineralize the enamel;
- reduction in the diet of the amount of products containing aggressive acids;
- end the meal with foods with neutralizing properties (hard cheese, milk, etc.).
Your teeth need constant care and attention. Only the prevention of their diseases will help maintain their healthy appearance. To do this, you need to visit the dentist every six months for examination and professional hygiene.