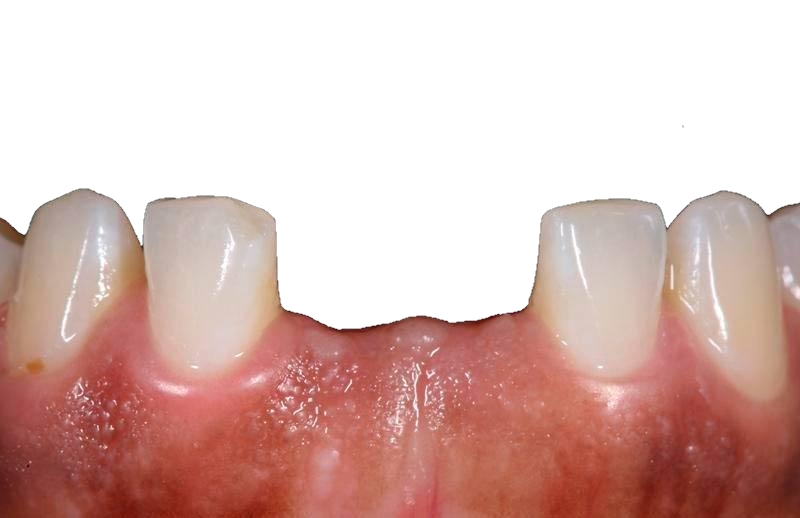
Adentia is a disease that leads to the complete or partial loss of teeth due to developmental disorders of the dentoalveolar system. With adentia, the integrity of the dentition is violated, speech and chewing functions worsen, cosmetic defects appear. In advanced forms, the disease leads to severe deformities of the facial bone, which leads to further loss of teeth.
How is the diagnosis carried out
The process of diagnosis and subsequent treatment consists in consulting such specialists as a periodontist, surgeon, orthopedist, implantologist and orthodontist.
The initial diagnosis is established on the basis of the collection and careful analysis of the patient’s complaints, as well as the clinical picture of the disease. The dentist also draws up a chronological picture of the disease, in which the main role is assigned to comparing the patient’s age and the number of teeth, as well as the nature of their absence.
Dentists can make an accurate diagnosis based on an x-ray examination of the oral cavity. An X-ray image allows you to determine the absence of teeth, identify roots, detect inflammatory processes, etc.
Based on the data obtained, a detailed treatment plan is developed.
Methods for the treatment of adentia
The most common technique for eliminating the consequences of adentia is prosthetics by installing fixed and removable orthopedic structures. The type of construction is chosen by the attending physician based on the physiological characteristics of the structure of the jaw.
Complete adentia of an acquired nature is also treated by the method of prosthetics, while removable systems are installed. If fixed systems are installed, then primary implantation of teeth is necessary as the basis for prostheses.
Partial adentia allows local installation of removable dentures. Artificial teeth are used only in places of loss of their own, which minimizes the complexity and duration of the procedure.