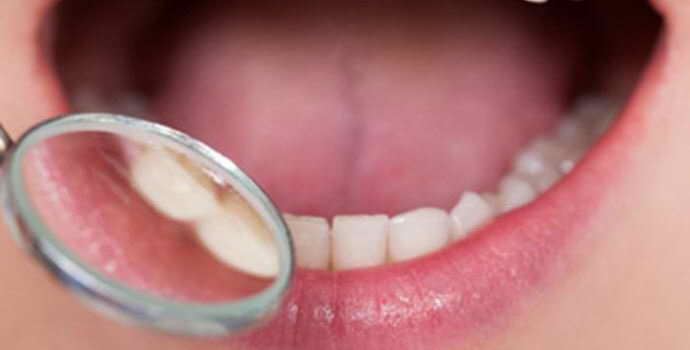
Stomatitis is a disease of the oral cavity, accompanied by inflammation of the mucous membrane and soft tissues. This disease is characterized by the appearance of redness, swelling, erosion and blisters. To diagnose and identify the cause of the disease, the doctor takes a smear from the affected area of the mucosa and conducts a deep analysis of it.
Stomatitis can be caused by a number of reasons:
- Exposure to bacteria and viruses that provoke infectious diseases;
- Unbalanced diet;
- Mechanical damage to the soft tissues of the oral cavity;
- Dehydration of the body;
- Poor or absent hygiene of teeth and gums;
- Poor quality of dentures installed in the oral cavity;
- Smoking;
- Avitaminosis;
- Hormonal disorders, etc.
The most common today is catarrhal stomatitis. It manifests itself in inflammation of the upper layers of the mucous membrane and is accompanied by sharp pains during meals, increased salivation, yellow plaque on the gums, etc. Catarrhal stomatitis, if left untreated, can develop into ulcerative, when not only the upper, but also all other layers of the mucous membrane are affected. In advanced cases, fever, general weakness of the body, and headaches are added to the above symptoms.
A decline in immunity can cause a sharp appearance of stomatitis. The mucous membrane begins to become covered with bleeding ulcers and erosions. An unpleasant putrid odor from the mouth appears, inflammation from the gums passes to the rest of the soft tissues of the mouth.
Stomatitis can act as an independent disease or be a symptom of another disease. To develop an effective treatment program, the doctor must conduct a comprehensive hardware diagnostics. Attempts at self-treatment can suppress the symptoms, but without the cause of the disease, it will only progress.